QUINOA, FEATURES AND BENEFITS OF A «SUPERFOOD»
For months I’m studying for a food that has for centuries cultivated and that our country is giving recently released. I’m really surprised by its many nutrients, benefits and properties and versatility in the kitchen, and you can include in our diet in many different ways. In fact it is a Super Food considered in NASA for its qualities.
It is rich in vegetable protein, vitamins E and B, calcium, essential amino acids, fiber, phosphorus, magnesium and iron; has healing and anti-inflammatory properties; no gluten, contains little fat and easy to digest. No wonder the “golden grain of the Andes” was already considered a sacred food for the native peoples of America.

Without wishing to bore you with a large amount of data, I would let you know Quinoa:
Scientific name: Chenopodium quinoa Willd.
Family: Chenopodiaceae
Name in different languages:
Aymara: Supha, jopa, jupha, Juira, ära, qallapi, vocali .
Chibcha: upload, pasca
Mapudungun: dawe, sawe
Quechua: ayara, kiuna, kitaqañiwa, kuchikinwa, amaranth, achita, qañiwa, qañawa.
English: quinoa, quinoa.
German: reisspinat, peruanischer.
French: anserine.
Italiano: quinoa, Chinua .
Portuguese: miúdo rice do Peru, quinoa.
A bit of History of Quinoa:
The Royal Quinoa, a grain of the Andes, noble product of the Pachamama, is one of the most important grains in the Andean region, which dates back to more than 5000 years, was the main food of pre-Columbian cultures, and corresponds to the needs and nutritional requirements of the modern world.
The quinoa or quinoa, known as the ” mother grain “in the Quechua language, quinoa was a staple of the I Incas for thousands of years, along with their religion and culture.
With the arrival of the conquistadors its cultivation was replaced by corn and potatoes; over time, its cultivation has been disappearing with the annihilation of the native culture. The quinoa has the highest rate of protein, calcium, phosphorus, iron and magnesium than other cereals. It also contains all essential amino acids, is rich in fiber and B vitamins and does not contain gluten.
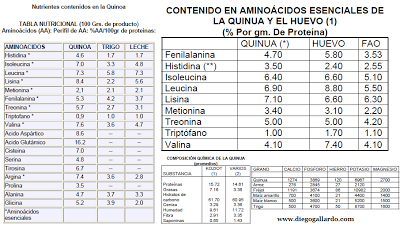
QUINOA AMINOACIDS :
Being a very digestive soft grain, quick cooking and noticeable taste, in addition to its nutritional properties, it is very easy to use and is available in myriad ways, beans, chips, flour, pasta, breads, cookies, different drinks meals.
It is called pseudocereal because it belongs to the family of grasses that are “traditional” cereals such as rice, oats, etc., for their high starch content corresponds to the use of a cereal.
It’s ideal amino acid content essential and essential fatty acids, quinoa should be considered a vegetable food of higher nutritional value .
I want to focus on their contribution Protein and Amino Acids:
In general, if a comparison between the nutrient composition of quinoa and is made of wheat rice and maize (which traditionally referred to in the literature as the grains of gold) can corroborate that the average values reported for quinoa are higher than the three cereals in the content of protein, fat and ash (Rojas et al ., 2010a).
The literature on human nutrition indicates that only four essential amino acids are likely to limit the quality of mixed human diets. These amino acids are lysine, methionine, threonine and tryptophan. Thus, if the essential amino acid content of quinoa with wheat and rice is compared, one can appreciate its great nutritional advantage: for example, for the amino acid lysine, quinoa has 5.6 grams of amino acid / 16 grams of nitrogen compared with the rice and wheat has 3.2 2.8 (Repo-Carrasco, 1998).
Between 16 and 20% by weight of a seed quinoa constitute valuable protein biological, including all amino acids, including essential, ie wherein the or AGENCY is unable to manufacture and therefore requires ingest with food. The values of the content of amino acids in the protein quinoa grain cover requirements recommended for preschool, school and adult (FAO / WHO / UNU, age amino acids 1985). However, the importance of proteins lies in the quality quinoa. Proteins are mainly quinoa albumin and globulin type. These have a composition similar balanced essential amino acid composition to the amino acid casein, milk protein. It has also been found that quinoa leaves are high quality protein. In addition, the leaves are rich in vitamins and minerals, especially calcium, phosphorus and iron.
One hundred grams of quinoa contain lysine nearly five times, more than twice as isoleucine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine and valine, and much larger amounts of leucine (all with the essential amino acids tryptophan) compared with 100 grams of wheat.
Furthermore it exceeds by in some cases in amounts of triple-histidine, arginine, alanine and glycine and contain amino acids not present in the wheat as proline, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, cysteine, serine and tyrosine (all nonessential amino acids.
The exceptionally rich in amino acids having properties quinoa gives very interesting therapeutic. This is because the bioavailability of lysine of quinoa, the most abundant in their seeds-essential amino acid, is very high while in wheat, rice, oats, millet and sesame is significantly lower.This amino acid that improves the function immune to assist in the formation of antibodies, promotes gastric function, assists in cell repair, is involved in the metabolism of fatty acids, helps the transport and absorption of calcium, and even seems to slow or prevent Vitamin C along with metastasis cancer, to name just a few of its many therapeutic activities.
In terms of isoleucine, leucine and valine participate together in energy production muscular, neuromuscular disorders improve, prevent liver damage and allow for balancing blood sugar levels, among other functions. With respect to methionine is known that the liver-s used to produce adenosi-methionine, a substance especially effective to treat liver diseases, depression, osteoarthritis, disorders brain, fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue, among other ailments. Potent agent also acts as detoxifying significantly decreases the levels of heavy metals in the body and has an important protection against free radicals.

Quinoa also contains interesting amounts of phenylalanine (a brain stimulant and main element of neurotransmitters that promote alertness and relieving pain and depression, among other functions), threonine (which is involved in the work of detoxification liver, participates in the formation of collagen and elastin, and facilitates the absorption of other nutrients) and tryptophan (immediate precursor of the neurotransmitter serotonin so it is used successfully in cases of depression, stress, anxiety, insomnia and compulsive behavior).
For Regarding the “non-essential” amino acids quinoa contains more than triple histidine wheat, substance itself is an essential change in the case of babies because the body can not synthesize into adulthood so it is highly recommended that children acquire it by feeding, especially in times of growth. It also has a slightly anti-inflammatory action and participate in the immune response system.
Arginine, meanwhile, is also considered an almost essential amino acid in infancy, childhood and adolescence because it stimulates the production and release of growth hormone, also to improve the activity of the thymus and T cells, participate in the growth and muscle repair, and be a protector and liver detoxifier. As for alanine is source of energy for muscle, brain and nervous system and glycine acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain and tranquilizer such as motor function regulator. In addition, proline – amino acid containing no other cereals such as wheat involved in the repair of joints, it is necessary for the healing of injuries and ulcers, appears to be effective for treating cases of impotence and frigidity, is cardiovascular protector and used in conjunction with lysine and vitamin C to prevent or limit metastasis cancer.
It is also common in current cereal aspartic acid (function improving liver and is essential for maintenance of the cardiovascular system), glutamic acid (involved in the production processes of energy for the brain and phenomena as important as learning, memory and neuronal plasticity), cysteine (protective liver by binding to heavy metals to facilitate their removal in addition to destroying free radicals and enhance the immune) system, serine (powerful natural moisturizing agent) and tyrosine (which has an important anti-stress effect and plays a key role in alleviating depression and anxiety, among other functions).
Quinoa is obviously the star food among people who want to have an increase in the consumption of protein and amino acids in a healthy way.
Finally, highlight the aspect that comes calories quinoa (another debate in recent years) and, if the quinoa fat.Well, quinoa has no cholesterol, no way fat in the body and its glycemic index is low; For this, studies have shown that eating quinoa for a diet helps regulate the digestive system and not fattening. All their nutritional benefits and culinary possibilities have made this seed every day more present in our food.
Diego Gallardo
Sources:
FAO
ARGENTINA ASSOCIATION OF Phytomedicine
Dr. Maria Teresa Olivero Muñoz
feed-salud.euroresidentes

THE HEALTH BENEFITS OF EGGS
También te puede interesar

EGGS QUESTION (Myths about egg whites and egg yolks)
diciembre 29, 2020
THE SCIENCE OF ABS WORKOUTS: PROVEN METHODS FOR OPTIMAL RESULTS IN YOUR SIX PACK
marzo 19, 2024